Theme:
Nano Summit 2022
The 39th Global Summit on Nanoscience and Technology invites nanotechnology researchers, nanoscience and nanotechnology investors, Nanoscientists, practitioners, policy makers, industry experts and members of professional bodies to send their abstracts for the conference. Nano Summit 2022 will be held during April 25-26, 2022 as a webinar.
This conference provides a wonderful opportunity for you to enhance your knowledge about the newest interdisciplinary approaches in nanoscience and nanotechnology. Moreover, the conference offers a valuable platform to create new contacts in the field of nanoscience and nanotechnology, by providing valuable networking time for you to meet great personnel in the field.
This Online event has taken the initiative to gather the world class experts both from Academic and Industry in a common platform at Nano Summit 2022 Conferences to share their recent research finding to the world and enlighten other esteemed delegates on latest trends in the field of Nanotechnology. We cordially invite all concerned people from different countries to come join us at our event and make it successful by your participation.
- Nanotechnology Professionals
- Directors of companies in the field of Nanotechnology
- Leading scientists
- Biomedical Engineering
- Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
- Professors
- Fellows or postdoctoral students
- Researchers, CEOs
- Business Delegates
- Doctors
- Young research scientists
- Nanotechnology Associations and Societies
- Manufacturing Medical Devices Companies
- Healthcare professionals
- Founders and Employees of the related companies
- Clinical investigators
Track 1: Nanoscience and Technology
Nanoscience and technology is a branch of science that examines systems and manipulates matter on atomic , molecular, and supramolecular scales (the nanometre scale). Nanoscience is the study of ultra-small structures and materials, as well as the unique and appealing properties these materials exhibit. It is the application and study of little objects that can be employed in a variety of sectors including as research, development, and material science. These particles have the power to control individual atoms. Nanotechnology offers enormous potential for providing novel solutions to a variety of difficulties in science, essentialism, material science, contingent, and therapeutic fields.
- Drug Delivery and Nano Particles
- Molecular Nanotechnology
- Bionanoscience
- Lipid Nanoparticles
- Nanofliuidics and Nanoionics
- Nanobiopharmaceutics
Track 2: Research on Covid-19 Medicine and Vaccine
At the end of 2019, a viral contagious disease emerged and quickly spread over the world. The global impact of the epidemic is terrifying, and it may not have hit its peak yet. As a result of mandatory quarantines and lockdowns, the human race is also in a state of crisis. Because nanoparticles (NPs) and viruses have comparable activity scales, Nanotechnology can be used to build vaccines and manipulate the immune system. Researchers in the field of nanomedicine have been studying the association between the ability of different Nano Systems and viral vectors to deliver genes and high infectivity for quite some time. Because NPs may duplicate the structural and functional properties of viruses, Nanotechnology may be the safest alternative to innovative vaccine development approaches. On the market are two nanoparticle-based vaccines.
- Nano-based vaccines
- Nanomaterials for surface decontamination
- Role of Nanotechnology in combating COVID-19
Track 3: Applications of Nanotechnology in Corona Virus Diagnosis & Treatment
Combating CoV infections is a major problem for healthcare systems. Because of the virus's high transmission rate and capacity to tolerate numerous mutations, Nanotechnology has significant potential in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of COVID-19. Antiviral medicine target delivery and treatment efficacy have been shown to improve with the use of nano-based formulations. Another intriguing option is a new generation of vaccines based on several types of nanomaterials that have higher antigen storage, target delivery, and controlled-release. Nanotechnology based solutions for COVID-19 disease management include the development of technologies for rapid, accurate, and sensitive detection, the production of effective disinfectants, the delivery of mRNA vaccines into human cells, and the delivery of antiviral drugs into the body.
- Nanosensors for diagnosing
- Nanoparticles in COVID-19 Testing
- Bio-Nano Interface Technology
- Nanotherapies for COVID-19 Management
- Biomedical Nanotechnology
- Nanomaterials
Track 4: Nanoelectronics and Nanophotonics
Nanoelectronics is the term for the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. These components are frequently only a few nanometers in size. The more difficult it is to manufacture electrical components, the smaller they grow. Nanoelectronics encompasses a wide range of materials and devices that have the property of being so small that physical processes modify their properties on a nanoscale. The workings of these devices are heavily influenced by interatomic interactions and quantum mechanical features.
Nanophotonics, sometimes known as nano-optics, is a field of nanotechnology that examines light's behaviour at nanoscale sizes and how nanometer-sized objects interact with light. Nanophotonics is a sub-discipline of nanotechnology that includes electrical engineering, optics, and optical engineering. Nanophotonic devices are needed to control the parameters of quantum emitters and improve their usefulness.
- Nanoelectronic Biomedical Devices
- Nanofabrication
- Molecular electronics
- Nanotube transistors
- Modern optics
- Mobile and fixed networks
- MEMS and NEMS Devices
- Micro/ Nanolithography and MOEMS
- Quantum dot photodetectors
- Surface micromachining
Track 5: Nanobiotechnology
The interface of biology and nanotechnology is referred to as "Nanobiotechnology." This field helps to bridge the gap between scientific research and a wide range of nanotechnology fields. Nanobiology enhances ideas by taking into account the nanoscale, nanodevices, and nanoparticle phenomena that occur in nanotech research.
- Impact of Nanobiotechnology
- Regulations of Nanobiotechnology
- Roller Nanoimprint
- Bionanoscience
- Ultrafast Nanoimprint
- Nanobiomolecular Engineering
Track 6: Nanosafety
All of the difficulties regarding nanotechnology's protection are referred to as "Nanosafety." Despite the fact that nanotechnology has been growing for nearly two decades, it is still regarded as a novel technology, and the health effects of nanomaterials have not been adequately investigated. The physicochemical properties of nanosized materials differ from those of the original material (thereby changing their reactivity in biological systems). It raises the question of whether conventional methods for assessing the detrimental effects of NMs are still valid.
- Genetic sequence using DNA-tagged gold nanoparticles
- Nanotechnology Regulations
- Carbon Nanotube Filters
- Strategic and Nuclear Disarmaments
- Disaster Management
Track 7: Green Nanotechnology and Water Treatment
Nanomaterials are incredibly small particles that range in size from 1 to 100 nanometers in size. Green nanomaterials or nanoparticles are made via biological methods. The synthesis of green nanoparticles is aided by natural resources such as plants, microorganisms, and organic polymers such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Green nanoparticles provide a new method to eliminate contaminants from water bodies. Green nanoparticles are a cost-effective, convenient, and environmentally friendly option for wastewater treatment.
Nanotechnology is a cutting-edge science that has the potential to solve the challenges related to the current water treatment issue. By allowing the most optimal use of eccentric water resources, it has the ability to provide new dimensions to present water treatment techniques. In water treatment, nanotechnology is utilised for three main purposes: remediation and purification (by removing all or part of the contaminants), pollution monitoring (by using pollutant-specific nanosensors and detectors), and pollution prevention.
- Nanotechnology in Water Treatment
- Water purification Technology
- Nanoremediation & water treatment
- Water filtration
- Nanosorbents water treatment
- Nanotech in disinfected water
Track 8: Nano Engineering
Nanoengineering is a field of engineering concerned with the study, development, and refinement of materials on a very small scale. It can be thought of as the practical application of nanoscience, similar to how mechanical engineering uses physics principles. Nanoengineering is the study of nanoparticles and their interactions with the goal of developing useful materials, systems, devices, and structures. Nanoengineering is a technique that has applications in a wide range of industries, including electronics, energy, medicine, and biotechnology. It is not a new science. A nanoengineer's work might be extremely varied, but it mainly centres around the development of nanomaterials. Quantum dots, carbon nanotubes, and nanocomposites are just a few examples.
- Nano Robotics
- Nano Devices
- Nano Sensors
- Nano Structures
- 3D Printing
- DNA Nanotechnology
Track 9: Nanotech: In other fields
Nanotechnology is a field of science that manipulates materials' molecular structure to change their inherent features and generate new ones with revolutionary applications. This is the case with graphene, a modified carbon nanoparticle that is harder than steel, lighter than aluminium, and virtually transparent, and is used in electronics, energy, healthcare, and defence. Nanotechnology is a growth industry in research and development around the world, and nanoparticles may already be found in a wide range of products, including sunscreens, cosmetics, fabrics, and sports equipment. Nanotechnology is being used to produce drug delivery, biosensors, and other medicinal applications.
- Computer Sciences
- Environmental Sciences
- Household Nanotechnology
- Biomedical Sciences
- Agricultural research
- Food Industry
Track 10: Nanotechnology Applications
Nanotechnology has the potential to improve the quality of our air, water, and energy generation, with substantial environmental consequences. The application of nanotechnology techniques to reduce or prevent environmental damage is known as environmental nanotechnology. Nanotechnology has the potential to have a positive impact on the environment by providing solutions for removing existing pollutants. Environmental nanotechnology has a lot of promise for improving the quality of life on our planet. By conserving raw resources, energy, and water, as well as cutting greenhouse gas emissions and hazardous waste, nanotechnological materials, methods, and applications are expected to make significant contributions to environmental and climate protection. As a result, using nanomaterials has some environmental advantages and long-term consequences. Nanotechnology, on the other hand, is now playing a little role in environmental protection, whether through research or development.
- Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment
- Nanotechnology in Tissue Engineering
- Nanostructured materials for construction
- Nanotechnology in Food Science
- Nanotechnology in Space
- Nanotechnology in Food manufacturing
- Nanotechnology in Electronics
- Nanotechnology in Energy
- Nanotechnology in Biomedicine
- Nanotechnology in Environment
- Nanotechnology in Textile Industry
Track 11: Nanotoxicology
Nanotoxicology is a developing field that has its roots in the environmental toxicity of ultrafine particles. Nanotoxicology is a branch of toxicology that investigates the toxicity of nanoparticles produced by industrial processes (such as spray drying or grinding), combustion processes (such as diesel soot), and naturally occurring processes (such as atmospheric reactions or volcanic eruptions). Nanoparticle toxicity varies with cell cycle and is more hazardous to some cell subpopulations than others. The goal of nanotoxicological study is to figure out how nanoparticles and nanopharmaceuticals affect people and the environment. Improving the quality of data presentation in nanotoxicology studies, particularly in the area of test item characterization, is a major priority for toxicological and scientific journals that publish findings from nanotoxicology investigations.
- Toxicological assessment of manufactured Nanoparticles
- Effects of Nanotoxicology in Nanomaterials
- Impacts of Nanoparticle design in Nanotoxicology
- Different types of Nanotoxicology
- Reduction in toxicity while maintaining therapeutic effects
Track 12: Carbon nanotechnology
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylinder-shaped molecules made of single-layer carbon atom sheets that have been rolled up (graphene). Carbon nanotubes are divided into two types: single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCN) . Multi-walled nanotubes (MWCN) have a diameter of more than 100 nm and are made up of numerous concentrically interconnected nanotubes. Single-walled nanotubes (SWCNT) have a diameter of less than 1 nanometer (nm). Their size might range from a few micrometres to many millimetres. Carbon nanotubes are one of the most durable materials known to man, having unique structural and electrical properties that make them ideal for a variety of applications.
- Carbon nanotubes formation and characterization
- Properties of Nanotubes
- Polymer-carbon nanocomposites to sensors
- Purification and separation of carbon nanotubes and related aspects
- Nano Electron emitters
- Molecular electronics
Track 13: Nanometrology
Nanometrology is a branch of metrology concerned with the science of measurement at the nanoscale level, including the quantitative determination of dimensions as well as other physical properties such as electrical, mechanical, optical, magnetic, and combinations thereof, chemical and biological properties of nanomaterials, and events occurring at the nanoscale level. It is derived from the Greek words "nanos," which means "one billionth," and "metrologia," which means "ratio theory." Nanometrology has only recently been recognised as a critical component of the future of nanotechnology in general, and the growth of the NP industry in particular. The study of measuring dimensions in nanomaterials and nanodevices is known as nanometry. Nanometrology is critical for industrial quality control and toxicity studies. If nanotechnology hadn't become so popular, it wouldn't have gotten to where it is now.
- Microfluidics and Nanofluidics
- Microscopy
- Nanotribology
- Nano coordinate measuring machine
- measurement techniques
- Surface area measurement
Track 14: Environmental Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology has the ability to significantly improve the quality of our air, water, and energy generation, resulting in significant environmental impacts. Environmental nanotechnology is the use of nanotechnology techniques to mitigate or prevent environmental degradation. Nanotechnology can have an impact on our environment by offering solutions to clean up existing pollutants. Environmental nanotechnology has a lot of potential for improving our planet's quality of life. Nanotechnological materials, methods, and applications are predicted to make major contributions to environmental and climate protection by conserving raw resources, energy, and water, as well as lowering greenhouse gas emissions and hazardous waste. As a result, using nanomaterials offers some environmental benefits and sustainable impacts. Nanotechnology, on the other hand, is now playing a little part in environmental protection, whether in research or in real - time applications.
- Nano-Enabled Treatment Technologies
- Nano-Sensors for Biological/Chemical Contamination
- Nanomaterials for Water, Soil and Air Remediation
- Nanopollutants
- Environmental Monitoring with Nanotechnology
Track 15: Pharmaceutical nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of structures with dimensions ranging from 0.1 to 100 nanometers. The building and development of small structures such as atoms, molecules, or compounds with sizes ranging from 0.1 to 100 nm into structures that can be further developed into unique devices with desired properties and qualities is the focus of pharmaceutical nanotechnology. In pharmaceutics, nanotechnology aids in the creation of more improved drug delivery methods, making it a valuable and potent tool as a replacement for traditional dosage forms. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology aids in the fight against a number of diseases by identifying disease-related antigens as well as the bacteria and viruses that cause them. It has proven to be helpful in overcoming the disadvantages of standard dosage forms like tablets.
- Nano Pharmaceuticals
- Biopharmaceutics and Liposomes
- Nano Drug Delivery
- Synthesis & exhaustive characterization of Pharmaceutical nanoparticles
- Biological evaluation
- Clinical testing and/or toxicological assessment
Track 16: Energy and Environment
The development of molecular-scale functional systems is what nanotechnology is all about. Nanotechnology is being used to improve the environment and produce more efficient and cost-effective energy in a variety of ways, including reducing pollution during material manufacturing, producing solar cells at a competitive cost, and cleaning volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the air and organic chemicals polluting groundwater. Nanomaterials and manufacturing techniques have been used in a variety of applications. Solar cells, fuel cells, secondary batteries, supercapacitors, air and water purification, and the eradication of indoor and outdoor air pollutants have all benefited from their use. New nanomaterials capable of offering the shortest reaction pathways and thus optimising reaction kinetics are commonly required for clean energy and environmental applications. Understanding the physicochemical, structural, microstructural, and optical properties of nanoparticles.
- Novel Generation in Energy storage
- Nonnuclear Materials
- Oil & Gas
- Nano-energy
- Nano Solar Cells
- Nanofuels
- Nano Batteries
- Nano fibers
Track 17: Nanocharacterization
Nanoparticle characterization is a subfield of nanometrology concerned with identifying and measuring the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are often designed for their unique properties and have at least one exterior dimension of fewer than 100 nanometers. Nanocharacterization is used for a variety of purposes, including occupational exposure evaluations to determine health and safety issues, nanotoxicology research, and process control.
- Nano Tribology
- Nano Sensors and Actuators
- Nanoscale Particles Microscopy
- Quality of Nanosystem
- Regulatory aspects towards Approval of Nanomedicine and nanostructures
Track 18: Life Sciences & Nanomedicine
Nanotechnology is the study and application of science and engineering at a scale of less than 100 nanometers (nm). Biological interactions take place at the nanoscale. A flood of nanotechnology-based applications are currently being studied, thanks to our expanding understanding of these interactions. Nanotechnology is becoming more widely applied in the life sciences. Medicines, biotechnology, and tissue engineering all are using nanoscale designs and architectures. With new technologies that improve drug administration and provide unique diagnostic processes, nanotechnology's application in medicine has a lot of potential. Different aspects of nanotechnology are bringing science's almost incomprehensibly small device closer to reality, and developments will eventually be so significant that they will affect all areas of research and technology.
- Medical Technology
- Nano-diagnostics, Imaging and nano-therapy techniques
- Cell Repair therapy
- DNA Nanotechnology
- Biomarkers and Biosensors
- Measurement of Health Risk
- Nanoproteomics and genomics
- Protein Nanocrystallography
- Organ-on-a-chip
Track 19: Nanochemistry and Wet Nanotechnology
Nanochemistry is a fast emerging branch of chemistry, particularly solid-state chemistry, that focuses on the development of useful materials with nanometer-scale dimensions (1–100 nm). It's a relatively young discipline of chemistry and materials science that focuses on finding new techniques to make nanoscale materials. Electronics and nanodevices and systems, composite materials, biotechnology and medicine, and even the textile industry have all been investigated using these materials.
Wet nanotechnology is a brand-new subfield of nanotechnology that will be dominated by various sorts of wet engineering. The techniques will take place in aqueous solutions and are quite similar to those used in biotechnology / bio-molecular production, which focuses on the manufacture of biomolecules like proteins and DNA/RN. The purpose of wet nanotechnology is to work up to huge masses from small ones (also known as wet nanotech). The presence of water in the process is necessary for wet nanotechnology. Chemists and biologists are also involved in the process, which involves bringing individual molecules together to achieve bigger scales.
- Graphene & Fullerenes
- Medicinal Nanochemistry
- Nanotechnology in clothing
- Brownian motion in wet nanotech
- Hydrophobic Nanotechnology
Track 20: Nano computational modeling
Nanotechnology is advancing fields as diverse as electronics, microcomputing, and biology, as well as health, consumer goods, aircraft, and energy generation. Improved modelling and simulation methodologies are required to gain a more rigorous quantitative understanding of matter at the nanoscale, as development in nanoscale science and engineering leads to the continual creation of sophisticated materials and creative technologies. Computational nanotechnology is an area of nanotechnology concerned with the development and use of computer-based models for understanding, analysing, and forecasting the behavior or characteristics of nanotechnology-related systems. Computational Nanotechnology provides expert insights into current and novel approaches, opportunities, and issues related to computational tools utilised in nano scale research.
- Computational Modelling of Photonic Nanomaterials and devices
- Catalytic Cycles and Reactions
- Stochastic motion of Nanomotors
- Optimisation Nanostructures
- Molecular Modelling and simulation of Nanoscale systems
- Foundation of Nanoscale Physics and Modelling
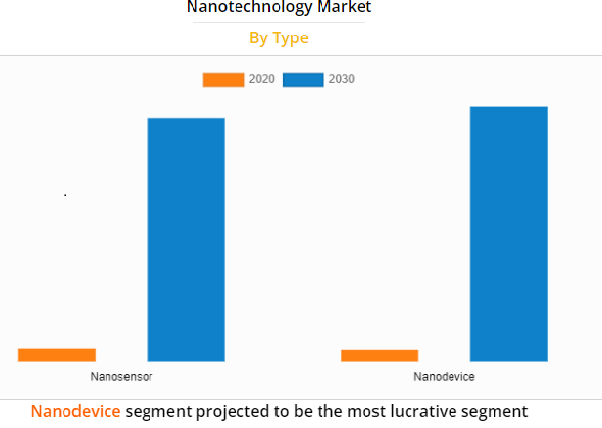
Nanotechnology Market Outlook – 2030
The nanotechnology market size was priced at $1.76 billion in 2020, and is expected to reach $33.63 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 36.4% from 2021 to 2030. Nanoscience and nanotechnology contain the study of nanoparticles and devices, which find their request across all the science fields such as chemical, bio-medical, mechanics, and material science among others. Nanotechnology market includes the invention and application of physical, chemical, and biological systems and devices at scales ranging from separate atoms or molecules to around 100 nanometers.
Nanotechnology transmits a significant impact, and helps as a revolutionary and beneficial technology across several industrial domains, including communication, medicine, transportation, agriculture, energy, materials & manufacturing, consumer products, and households. Emerging use cases and request is estimated to be one of the key factors donating towards the growth of nanotechnology market size. The U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative has expected that around 20,000 researchers are working in the field of nanotechnology. For the UK, the Institute of Occupational Medicine has expected that approximately 2,000 people are employed in new nanotechnology companies and universities where they may be potentially visible to nanoparticles.
In addition, Nano scale sensors and devices may provide cost-effective constant monitoring of the structural reliability and performance of bridges, tunnels, rails, parking structures and paths over time.
Moreover, Nano scale sensors, communications devices, and other innovations permitted by Nano electronics support an improved transportation infrastructure that can communicate with vehicle-based systems to help drivers maintain lane position, avoid collisions, adjust travel routes to avoid congestion, and improve driver’s borders to on-board electronics. All these factors are estimated to be major nanotechnology market trends globally.
Factors such as flow in approval of nanotechnology in medical diagnosis & imaging, and technical advancements in nanotech devices drive the development of the global nanotechnology market. However, issues rising in the placement of Nano devices in risky conditions and high cost of the technology act as the major barriers, thereby hampering the market growth. On the contrary, increase in support and R&D funding from government organizations and emergency of self-powered nanotech devices are estimated to offer beneficial opportunities for the nanotechnology market prediction.
Conference Highlights
- Nanoscience and Technology
- Research on Covid-19 Medicine and Vaccine
- Applications of Nanotechnology in Corona Virus Diagnosis & Treatment
- Nanoelectronics and Nanophotonics
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nanosafety
- Green Nanotechnology and Water Treatment
- Nano Engineering
- Nanotech: In other fields
- Nanotechnology Applications
- Nanotoxicology
- Carbon nanotechnology
- Nanometrology
- Environmental Nanotechnology
- Pharmaceutical nanotechnology
- Energy and Environment
- Nanocharacterization
- Life Sciences & Nanomedicine
- Nanochemistry and Wet Nanotechnology
- Nano computational modeling
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | April 25-26, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | ||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by